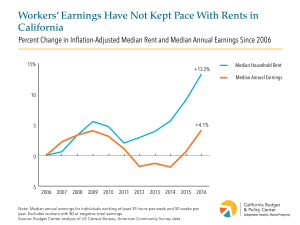
A new report from the California Budget & Policy Center paints a grim picture about the impact housing has on rising rates of poverty in our state.
California continues to have one of the highest poverty rates among the 50 states, statistically tied for first with Florida and Louisiana, according to new Census data released this morning based on the Supplemental Poverty Measure (SPM). This poverty measure provides a more accurate indicator of economic need in California than the official federal poverty measure because it accounts for the high cost of living in many parts of the state, among other factors.
The new data show that about 7.5 million Californians — nearly 1 in 5 state residents (19.0%) — do not have enough resources to cover the costs of basic necessities. High housing costs are a key reason for California’s high SPM poverty rate, underscoring the need to increase access to affordable housing within the state. The new data also show the critical role played by public supports like tax credits, food assistance, and disability benefits in reducing poverty at the national level. Protecting and strengthening these supports is vital to bringing down California’s high poverty rate. State lawmakers have taken recent steps to bolster supports like the CalEITC, California’s refundable tax credit for working families, and CalWORKs, the state’s welfare-to-work program. National policymakers, on the other hand, over the past year have proposed changes to public supports that would reduce their effectiveness in addressing poverty, including changes currently being considered to the most important public source of food assistance.
Read the full report from the California Budget & Policy Center here.



